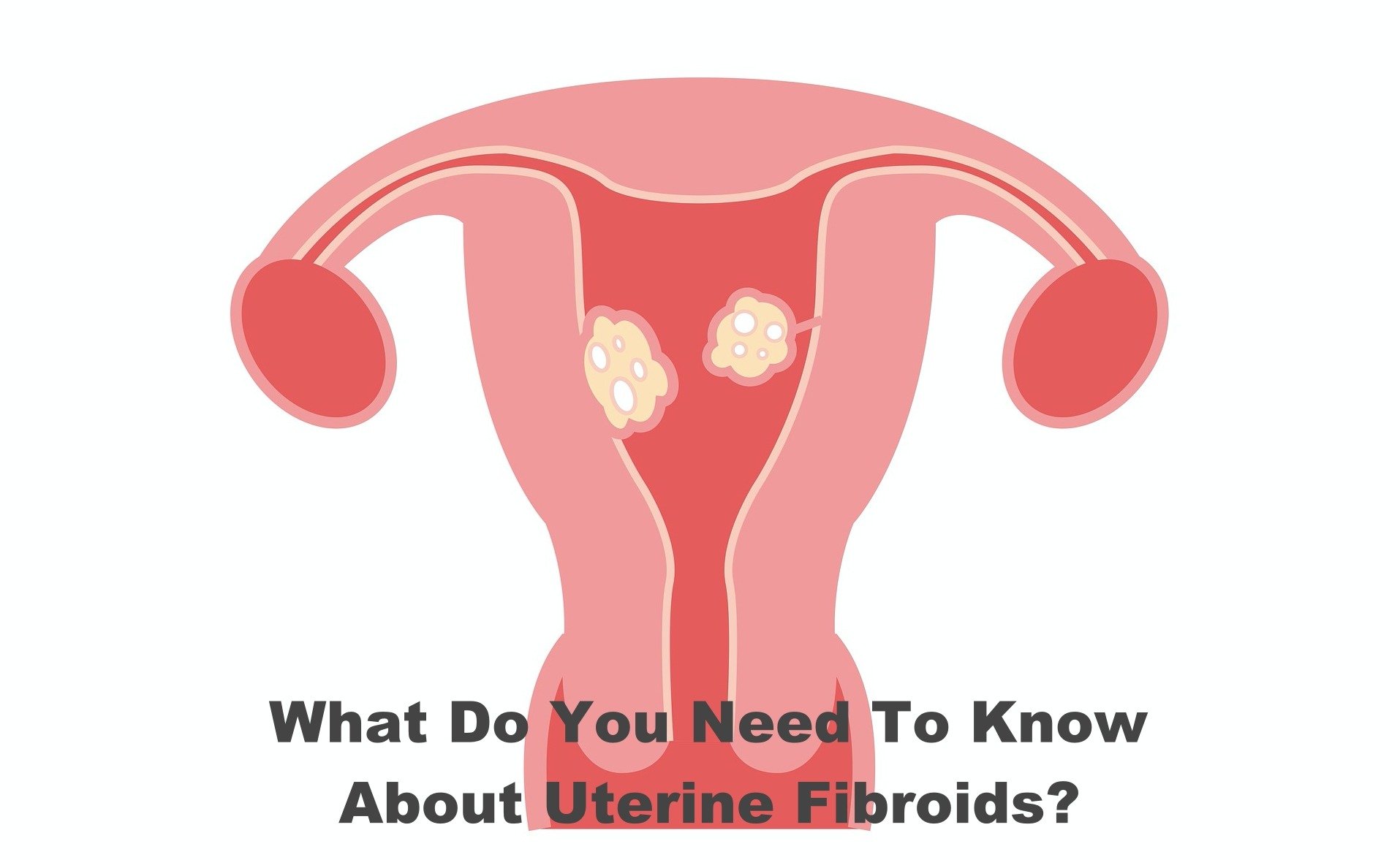
Uterine Fibroids are generally benign growths that mostly appear inside or on the uterus. These are mostly seen in women that are of childbearing age. Uterine Fibroids are also known as myomas, leiomyomas, uterine myomas, and fibromas.
Uterine Fibroids are not a cause of concern as they rarely develop into uterine cancers. However, they do cause a lot of discomfort like pain in the abdominal area and heavy bleeding during periods, which is when they become enlarged in size. Uterine Fibroids can vary in size, and sometimes these are so small that they cannot be seen with the naked eyes, and sometimes they get so big that they can even push at the wall of the uterus thereby enlarging it.
The number of uterine fibroids also varies from person to person, and sometimes they appear just as a single one while sometimes there are just so many of these. In rare cases, it also happens that they grow so much in number that they even touch the rib cage.
Almost every woman develops uterine fibroids at some point in their lives, but in the absence of symptoms, it cannot be ascertained unless the doctor performs a pelvic exam or an ultrasound. According to the National Institutes of Health or NIH, by the age of 50, almost 80 per cent of women develop uterine fibroids.
Symptoms
A lot of women that have uterine fibroids do not exhibit any symptoms, but when the symptoms do show up, these depend on a lot of factors like how many tumors there are in total, their size, and location. Those women that suffer from submucosal fibroids experience heavy bleeding during periods and also have difficulty in getting pregnant including seven other signs. Those women that are going through menopause and have fibroids that are small in size do not exhibit any symptoms of uterine fibroids.
The growth of uterine fibroids depends on the level of hormones in the body like estrogen and progesterone. Therefore women who are going through menopause or are post-menopausal in them if they have fibroids due to low levels of these hormones in their body the fibroids tend to shrink in size.
The most commonly seen symptoms of uterine fibroids are:
- bleeding heavily between periods or during periods with blood clots
- feeling the need to urinate quite frequently
- pelvic and lower back pain
- extremely painful periods
- pain while having sex
- periods that last longer than a week
- the feeling of fullness in the lower abdominal area
- engorgement of the abdominal area
- pain in the legs
- constipation
Types of Uterine Fibroids
The type of fibroids that a woman develops highly depends on its location, meaning whether it appears inside the uterus or on its outer surface. The various types of uterine fibroids are:
-
Intramural fibroids
These are the most common type of fibroids that women suffer from. The location is generally the inside of the uterus. Intramural fibroids can grow big and can distort the shape of the uterus by pushing at its walls.
-
Subserosal fibroids
Subserosal fibroids appear on the outer surface of the uterus, which is also known as a serosa. If they grow in size, they might make the uterus seem heavier on one side.
-
Pedunculated fibroids
When Subserosal fibroids appear with a stem that is attached to the surface of the uterus, these are known as Pedunculated fibroids.
-
Submucosal fibroids
Submucosal fibroids appear in the inner walls of the uterus, which is known as myometrium. Unlike other types of uterine fibroids, the submucosal type of fibroids are rarely seen.
What Causes Uterine Fibroids?
The exact cause as to why women develop uterine fibroids is still very much unknown; however, certain factors encourage the development of them. These are:
-
Hormones
The menstrual cycle is controlled by two hormones, namely estrogen, and progesterone. These help in the development of the uterine lining to prepare for a possible pregnancy, which when it does not happen sheds in the form of periods. It has been seen that these two hormones are the main cause for the development of uterine fibroids. Uterine fibroids are seen to contain progesterone and estrogen receptors, unlike the normal uterine lining that does not seem to have these receptors. It has been seen that in women that are going through menopause, the size of uterine fibroids greatly shrinks due to the low levels of these two hormones.
-
Genetics
Because uterine fibroids run in the family, there is a greater chance for a woman to develop them if their mother, grandmother, or sister suffered from them.
-
Pregnancy
Pregnant women are more susceptible to developing uterine fibroids during pregnancy, and there is a surge of the hormones estrogen and progesterone in the body.
-
Certain growth factors
Certain substances in the body that help in the maintenance of the tissues, for example, growth factors like insulin might cause uterine fibroids to develop.
-
Extracellular matrix or ECM
The Extracellular matrix is a substance that helps the cells to stick together. It makes uterine fibroids fibrous, and they also consist of certain types of growth factors that cause biological changes within the cells.
According to doctors, uterine fibroids form from a stem cell located in the smooth tissue of the uterus, also known as myometrium. One single stem cell starts growing abnormally and develops into a mass that is different from the tissues around it. Uterine fibroids sometimes grow at a very high speed while sometimes they grow very slowly. In some cases, they even stay the same size. In pregnant women that have uterine fibroids after delivery, it has been seen that the fibroids go away on their own.
What Are The Risk Factors & Complications?
Uterine fibroids are generally seen in women that are of childbearing age, but other than that some risk factors that increase the chances of developing these.
-
Race
Black women are more likely to develop uterine fibroids than women of other races. It is also seen that black women develop fibroids at a much younger age, and they also tend to be larger in size. Additionally, black women suffer from severe signs and symptoms, as well.
-
Heredity
Since uterine fibroids run in the family, there is a great chance for a woman to develop these if their sister, mother, or grandmother suffered from it. Other risk factors that increase the chances of developing uterine fibroids are:
- having periods at a very young age
- being overweight
- deficiency of Vitamin D
- Eating a meat-rich diet with a very low amount of vegetables
- alcohol consumption including beer
- having more dairy and fruits in the diet
Complications of Uterine fibroids
Uterine Fibroids are benign, and so they do not pose a serious risk, but they cause a lot of discomforts, which also leads to developing certain complications, including anaemia or low levels of red blood cells due to heavy bleeding during periods which causes the patient to experience extreme fatigue. In some extreme cases, a blood transfusion is needed to make up for the loss of blood.
Developing fibroids during pregnancy
In general uterine fibroids do not interfere with conception, but some types of uterine fibroids may prove to be a hindrance in conceiving. For example, the submucosal fibroids that develop in the inner muscular tissue of the uterus might cause a woman to be infertile. Uterine fibroids can cause certain complications in pregnant women like abruption of the placenta, early delivery, restricted growth of the fetus.
Treatment
Based on the size of the fibroids, age, and overall health of the patient, the doctor will start a treatment plan.
-
Treatment of uterine fibroids with the help of home remedies
Among some of the home remedies that have been shown to have a positive effect on fibroids include Yoga, Acupuncture, and Gui Zhi Fu Ling Tang.
GFLT or Gui Zhi Fu Ling Tang which is a traditional Chinese formula of the medicinal application of heat when experiencing cramping (this should be avoided while experiencing heavy period bleeding). Along with these remedies, following a good diet can also have a lot of positive effects on fibroids. The diet should include lots of green vegetables, green tea, fish such as salmon and tuna, and foods that are rich in flavonoids. Along with that, if a woman is obese, losing the extra weight can also help with fibroids, and also stress management can also be of great help.
-
Treatment of Uterine fibroids with medicine
For uterine fibroids, doctors may prescribe certain medicines that help in regulating the amount of hormones in the body as a way to shrink the size of the fibroids. GnRH or Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists like leuprolide or Lupron helps in bringing down the level of estrogen and progesterone in the body, which causes the periods to stop and thus shrinks the size of the fibroids.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists like cetrorelix acetate or Cetrotide and ganirelix acetate helps in shrinking the size of fibroids as well. They are able to do that by not letting the body produce the FSH or follicle-stimulating hormone and the luteinizing hormone (LH).
Some other options which can help while experiencing heavy bleeding and pain without causing the fibroids to shrink in size or get rid of them are:
- progestin releasing intrauterine device or IUD device
- pain delivers like ibuprofen which can be bought over the counter
- birth control medicines
-
Treatment of Uterine Fibroids with the help of surgery
The removal of fibroids with the help of surgery is known as myomectomy. It is usually performed on someone that is suffering from multiple uterine fibroids or when they are very big in size. The surgery involves an incision in the abdominal area through which the fibroids are removed. Myomectomy can also be done laparoscopically or with the help of small-sized incisions from where a camera and surgical tools are then inserted to remove the fibroids. A person might develop fibroids again after surgery.
-
Treatment of uterine fibroids using less invasive methods
With the help of forced ultrasound surgery or FUS, the fibroids are destroyed using high frequency and high energy sound waves. Another method is with the help of myolysis, which helps in shrinking the fibroids in size with the help of a laser. Cryomyolysis is another non-invasive method of treating uterine fibroids, which involves freezing these. Endometrial ablation is another method of treating fibroids; it involves the insertion of a special tool in the uterus in order to destroy the uterine lining using hot water, electric current, and heat.
https://embrywomens.wpengine.com/uterine-fibroids-faq-074/
Final Thoughts
Uterine fibroids are very common, and these are nothing to be afraid of as they are mostly benign in nature and rarely turn into cancer. The causes of fibroids are still not known, and so these cannot be prevented. There are, however, certain things that women can do that can help reduce the risk of them developing these in the first place, which includes having a healthy lifestyle, losing weight if they are obese, and managing stress.